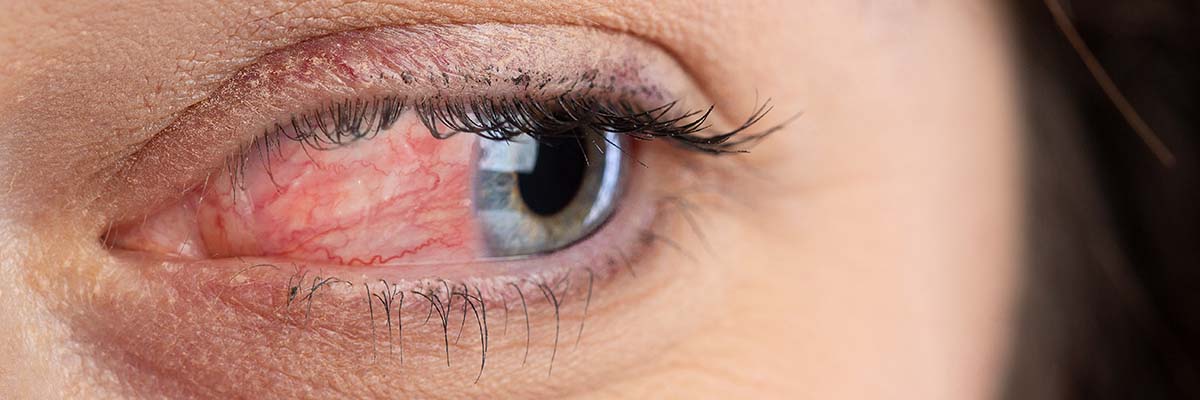
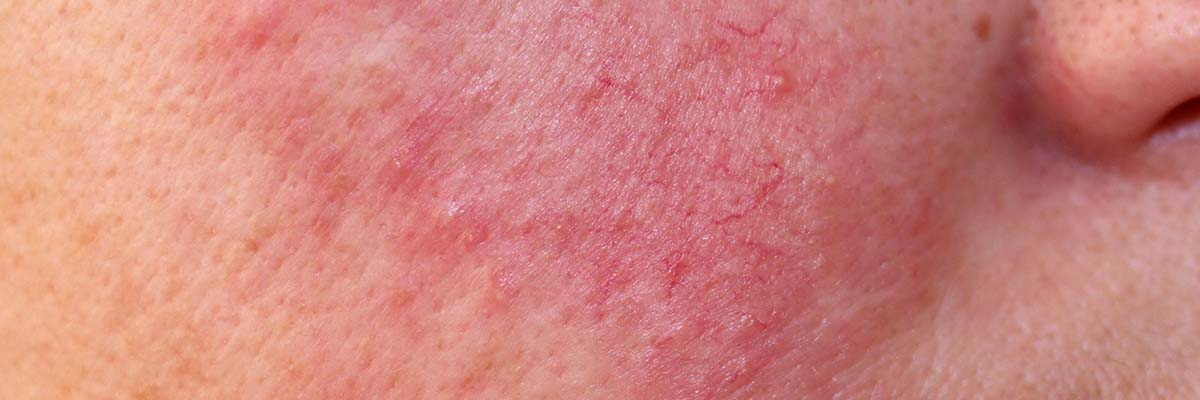
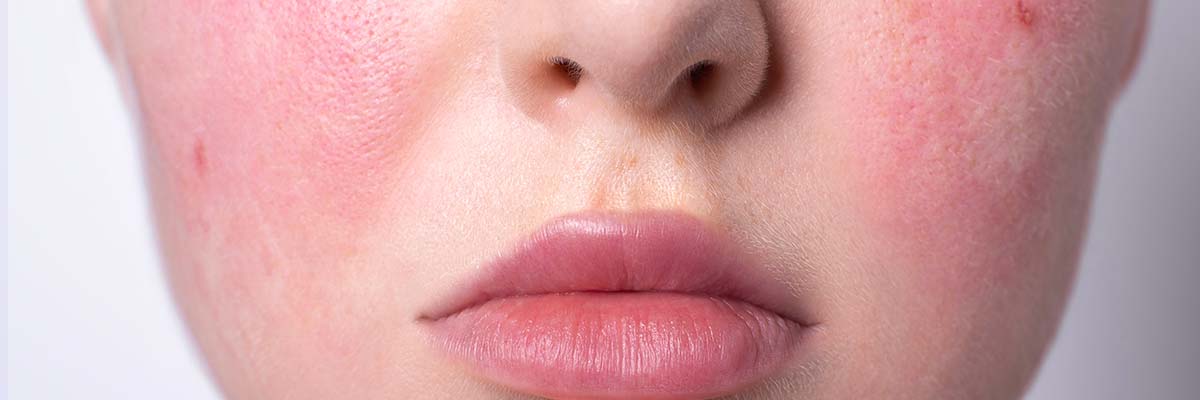
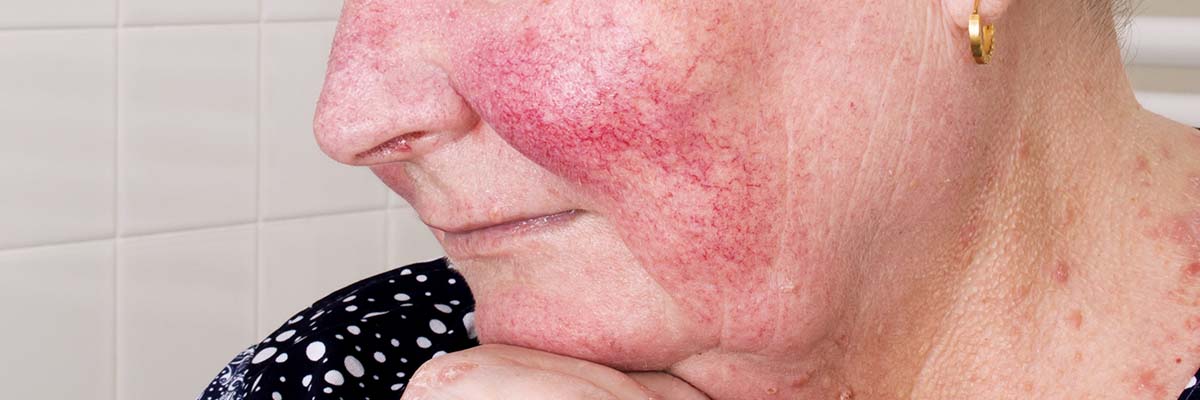
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that is characterised by persistent redness, flushing, visible blood vessels, and bumps on the face.
Rosacea can be accompanied by symptoms such as burning or stinging sensations and increased sensitivity to certain triggers like sunlight, spicy foods, alcohol, and stress.
The exact cause of rosacea is unknown but factors, including genetics, abnormal blood vessels, immune system abnormalities, and facial mites, may contribute to its development.
There are several types of rosacea, these include:
- Subtype one, which involves redness and flushing
- Subtype two, which includes papules and pustules
- Subtype three, which involves skin thickening
- Subtype four, which affects the eyes.
While there is no cure for rosacea, it can be managed with various treatment options based on the severity and subtype of the condition.
It is important for individuals with rosacea to collaborate with a dermatologist to develop an individualised treatment plan and research the best option to suit your needs.
Rosacea Dos
Sun protection
Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen every day. Wear protective clothing, such as hats and sunglasses when exposed to sunlight.
Gentle skincare routine
Use mild, non-irritating cleansers, moisturisers, and skincare products. Avoid harsh scrubs, astringents, and abrasive or irritating ingredients that may trigger flare-ups.
Use anti-inflammatory ingredients including niacinamide, allantoin, green tea and azelaic acid.
Identify and avoid your triggers
Keep a skin journal to track your flare-ups and identify triggers such as certain foods, beverages (e.g., alcohol or hot drinks), weather conditions, stress, or specific skincare products. Once identified, try to avoid, or minimise exposure to these triggers.
Stress management
Practice stress management techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or engaging in activities that help you relax.
Rosacea Don'ts
Avoid irritating or harsh products
Products that contain alcohol, fragrance, menthol, or certain acids (such as salicylic acid), can aggravate the skin and trigger flare-ups.
Avoid using acne treatments such as benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid as they are too drying for the skin and can worsen rosacea.
Over wash or scrub your face
Excessive washing or scrubbing can irritate the skin and worsen rosacea symptoms. Gently cleanse your face with cool water and a mild cleanser.
Do not forget to moisturise
Moisturising helps maintain the skin's barrier function and can reduce dryness and irritation associated with rosacea. Choose a lightweight, non-comedogenic moisturiser suitable for sensitive skin.
Do not pick or squeeze your skin
Avoid picking at or squeezing your skin as it can further irritate the skin and lead to potential infection and scarring.
Ingredients that help Rosacea sufferers
Here are some ingredients that have been suggested to have potential benefits for managing rosacea.
Azelaic Acid
This ingredient has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, which can help reduce redness and control breakouts associated with rosacea.
Green Tea Extract
contains polyphenols and antioxidants that can help reduce inflammation and soothe irritated skin.
Niacinamide
Also known as vitamin B3, has anti-inflammatory properties that can help alleviate redness and improve the skin's barrier function.
Liquorice Extract
Contains anti-inflammatory compounds that may help reduce redness and calm the skin.
Aloe Vera
Has soothing properties that can help reduce inflammation and alleviate skin sensitivity and irritation.
Caffeine
Studies suggest that topical caffeine can help constrict blood vessels and reduce redness associated with rosacea.

How your diet and gut health affects your skin
Rosacea is not an autoimmune condition, however there is a link between rosacea to gastrointestinal autoimmune diseases like celiac disease, reflux, SIBO (small intestine bacterial growth) and irritable bowel disease.
Research suggests the gut-skin-axis (the direct relationship between your gut and your skin) plays a significant role in the onset and development of rosacea. Although further studies are still ongoing with how the exact mechanisms are linked, what is for certain is when any aspect of your delicate microbiome is out-of-balance, the health of your entire body can suffer – including the health of your skin.
While there is no one-size-fits-all diet for rosacea sufferers, certain dietary changes may help manage symptoms and reduce flare-ups. Here are general recommendations that may be beneficial.
Avoid trigger foods
Common trigger foods for rosacea include spicy foods, alcohol, hot beverages, and foods high in histamine. It may be helpful to keep a food diary and identify any specific foods that worsen your symptoms.
Consume Anti-inflammatory foods
Including anti-inflammatory foods in your diet may help reduce inflammation associated with rosacea. These include fruits and vegetables, fatty fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids such as salmon, healthy fats like olive oil and avocados, whole grains, and nuts.
Probiotics
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome. Studies suggest that probiotics may have a positive effect on rosacea by improving gut health and reducing inflammation. Probiotic-rich foods include yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi.
Hydration
Staying well-hydrated is important for overall skin health. Drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day can help keep your skin hydrated and may reduce the risk of flare-ups.