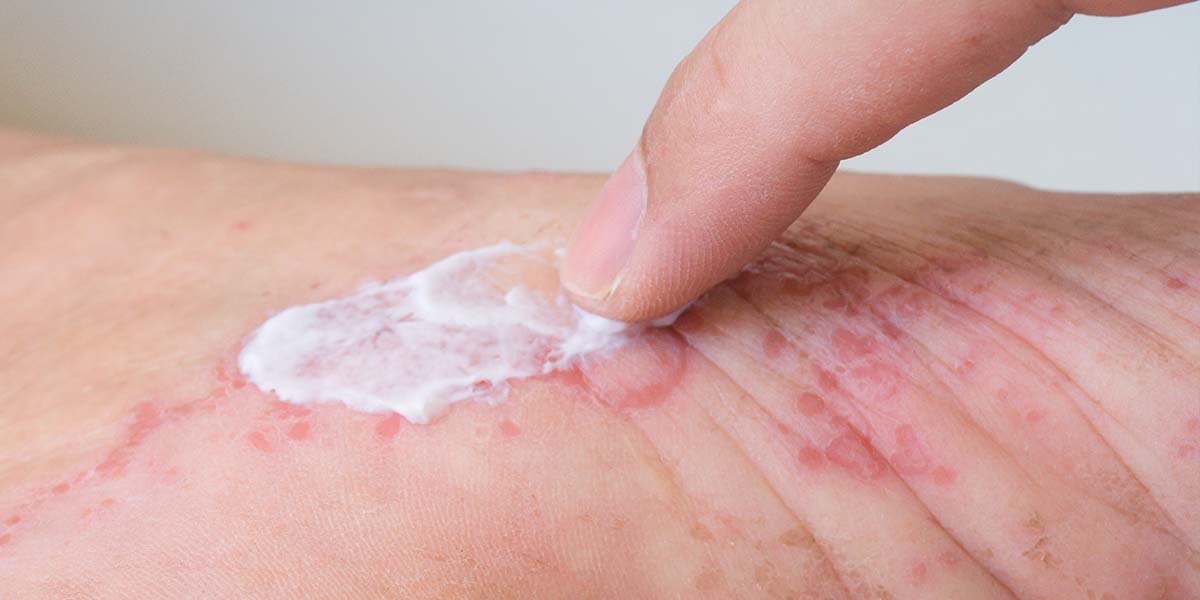
Immunosuppressants are medications that reduce or suppress the activity of the immune system. These drugs are often used to treat autoimmune diseases, manage inflammatory conditions or to prevent the body from rejecting transplanted organs, examples include:
- Organ Transplants: To prevent the immune system from rejecting a transplanted organ, like a kidney, heart, or liver. The immune system may see the transplanted organ as foreign and attack it. Immunosuppressants help prevent that.
- Autoimmune Diseases: In conditions where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues (like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or multiple sclerosis), immunosuppressants can help reduce inflammation and prevent further damage.
- Allergic Reactions: For severe allergies or conditions like asthma, where inflammation is a major problem, immunosuppressants can help control symptoms.
- Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: For conditions like Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis, which involve inflammation in the digestive tract, immunosuppressants can be used to manage flare-ups and reduce long-term damage.
Immunosuppressants are powerful drugs, and because they suppress the immune system, they can increase the risk of infections or other complications.
You should always be well informed before commencing any medications.
There are different types of immunosuppressants, including:
- Corticosteroids (prednisone)
- Calcineurin inhibitors (such as tacrolimus and cyclosporine)
- Antimetabolites (azathioprine and mycophenolate)
- Biologics (for example, TNF inhibitors like infliximab)
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are used to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. These medications can be taken orally, inhaled, applied topically, or injected, depending on the condition being treated.
Corticosteroids can be effective in relieving symptoms of eczema, psoriasis and dermatitis. Corticosteroids suppress the activity of some immune cells, which can interrupt the inflammatory process and prevent itching, redness, and swelling.

Types of corticosteroids to treat eczema or dermatitis
There are different types of topical corticosteroids, and doctors typically start with a lower-potency steroid for sensitive areas and may use a higher-potency one for thicker skin or more stubborn flare-ups. Some examples of topical corticosteroids include:
- Hydrocortisone (a mild steroid) – often used for mild eczema or dermatitis.
- Triamcinolone or betamethasone (moderate to strong steroids) – for more severe cases.
- Clobetasol (a very potent steroid) – used only in specific cases and for short periods due to its strength.
Your healthcare provider may also prescribe medicines in severe cases. The following are commonly used to treat atopic dermatitis:
- Antihistamines. Some examples include diphenhydramine and hydroxyzine to help ease itching. They may cause drowsiness.
- Oral antibiotics. Scratching the affected skin can bring bacteria to the area and this can lead to infection.
- Oral cyclosporine. This medicine has been used for years to treat atopic dermatitis that does not respond to other treatments. It has many side effects that should be considered carefully.
- Phototherapy. Two types are used to treat atopic dermatitis: ultraviolet (UV) light therapy and PUVA (chemo phototherapy). Light therapy uses UV light of specific wavelengths to target the immune system. It stops the responses that lead to inflammation.
- Topical immunomodulator. Also known as topical calcineurin inhibitors. They are put on the skin to change the immune response.
- Methotrexate. An immunosuppressive medicine that can be used to manage atopic dermatitis long term. However, it can potentially harm the liver.

Side Effects of Corticosteroids
Topical steroid withdrawal, sometimes referred to as ‘red skin syndrome’, can occur when frequently using or misusing moderate to high potency corticosteroids then stopping, either abruptly or reducing the dose too quickly.
Withdrawal symptoms include swelling, redness, burning, and skin sensitivity and this starts usually within 1-2 weeks of stopping the steroid.
Some of the more common side effects of cortisol-like drugs include:
- thin skin
- susceptibility to bruising
- high or increased blood pressure
- susceptibility to infections
- build-up of fat around the face, chest and abdomen
- fluid retention (oedema)
- diabetes.
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors
Topical calcineurin inhibitors (TCIs), such as tacrolimus (Protopic) and pimecrolimus (Elidel), are non-steroidal immunosuppressant medications used to treat skin conditions like eczema and seborrheic dermatitis.
They work by suppressing the immune response in the skin, reducing inflammation and helping to manage symptoms like redness, itching, and irritation.
Doctors often prescribe calcineurin inhibitors for people who need longer-term control of eczema but want to avoid the side effects of long-term steroid use.
Benefits of TCIs:
- Non-steroidal: Unlike corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors do not have the same risks of skin thinning, stretch marks, or other steroid-related side effects when used long-term.
- Safe for Sensitive Areas: They are often used for sensitive skin areas, like the face or skin folds, where corticosteroids should be avoided or used with caution.
- Effective for Maintenance: They can be used for longer periods than topical steroids for maintaining control over flare-ups or preventing them from occurring.
Side Effects of TCIs:
While generally well-tolerated, topical calcineurin inhibitors can have some potential side effects, including:
- Burning or stinging at the application site, especially after the first few applications.
- Skin irritation or redness in some people.
- Increased risk of infections (although the risk is lower compared to steroids).
- There have been warnings about a potential link to a very small increased risk of lymphoma or skin cancer, but this risk is still being studied and is generally considered rare.
Elidel, like other immunosuppressive treatments, should be used with caution, and it is generally recommended for short-term or intermittent use to manage flare-ups
Please read about the FDA's Black-box warning for these medications here.

Janus Kinase Inhibitors
Janus kinase inhibitors (JAK inhibitors) are a type of medication that target specific enzymes called Janus kinases (JAKs). These enzymes play a key role in the signaling pathways that regulate the immune system and inflammation.
JAK inhibitors are used to treat various autoimmune and inflammatory conditions, including:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: To help reduce joint pain, swelling, and damage caused by the overactive immune system.
- Psoriatic Arthritis: A form of arthritis that occurs in people with psoriasis, causing joint pain and skin inflammation.
- Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, where the immune system attacks the digestive tract.
- Eczema: JAK inhibitors have been approved to treat moderate-to-severe eczema in cases where topical treatments are not enough.
- Other Skin Conditions: Including Alopecia areata, Vitiligo and Plaque psoriasis
Side effects of Janus kinase inhibitors
As Janus kinase inhibitors alter the immune response, they may be associated with increased risk of serious bacterial, fungal, mycobacterial, and viral infections. Common adverse side effects of JAK inhibitors include:
- Nasopharyngitis
- Infection of upper respiratory and urinary tracts
- Headache
- Nausea and diarrhoea
Dupixent
Dupixent is an injection biologic medication used to treat several chronic inflammatory conditions where the immune system is overactive. It works by targeting and inhibiting the activity of two proteins involved in inflammation—interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interleukin-13 (IL-13)—which are responsible for much of the inflammation in conditions such as eczema and asthma.
Dupixent to treat Eczema
Dupixent is used for moderate-to-severe eczema. It helps reduce inflammation, itching, and skin lesions, particularly for people who have not responded to topical treatments like steroids.
Dupixent to treat Asthma
Dupixent is prescribed for moderate-to-severe asthma in adults and children (age 6 and older) whose asthma is driven by Type 2 inflammation. It helps reduce asthma attacks, improve lung function, and lower the need for oral steroids in people with uncontrolled asthma.
Side effects of Dupixent
- joint pain.
- reactions at the injection site, such as pain and swelling.
- cold sores.
- skin rash
- throat pain or soreness.
- insomnia
- toothache.
Potential serious side affects
Allergic reactions. Dupixent can cause allergic reactions that can sometimes be severe.
- breathing problems or wheezing
- fast pulse
- fever
- swollen lymph nodes
- swelling of the face, lips, mouth, tongue, or throat
- hives
- nausea or vomiting
- fainting, dizziness, feeling lightheaded
- abdomen cramps
Immunosuppressant Overview
Side effects vary greatly for the many different immunosuppressant medications available.
All immunosuppressant drugs carry the risk of infection. To find out the possible side effects you may be at risk of, always consult with your doctor.
Immunosuppressant drugs can cause problems for people with certain health conditions. Tell your doctor if you have any of these conditions before you start to take immunosuppressants:
- allergy to the specific drug
- history of shingles or chickenpox
- kidney or liver disease
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Some immunosuppressant medications can cause birth defects. In any case, if you are planning to become pregnant, talk to your doctor before taking an immunosuppressant drug.
If you fall pregnant while taking an immunosuppressant, tell your doctor right away.
The AMPERNA® Skin Solution
When it comes to skin health, Kiri, founder of AMPERNA®, helps many people suffering from a variety of skin & health conditions.
If you need topical steroid usage support or help with steroid withdrawals, you can sign up to Holistic Coaching with Kiri as she has extensive knowledge on oral and topical steroid withdrawals. And there are also steroid withdrawals support groups via ITSAN.
The probiotic complex infused within AMPERNA® products supports the skin barrier, helping to protect you from aggressions such as environmental pollutants, keep your immune system in check and reduce inflammation.
AMPERNA® products deliver good bacteria to your skin gently and effectively & create the perfect conditions for your skin to breathe & shine.
References:
Immunosuppressant Drugs: A Complete Overview (healthline.com)
Hormones – cortisol and corticosteroids - Better Health Channel
Immunosuppressants: Definition, Treatment & What Is It (clevelandclinic.org)
Medication for Eczema & Dermatitis | NYU Langone Health
Immunosuppressants: Uses, Side Effects, Precautions (verywellhealth.com)
Eczema | Johns Hopkins Medicine
Atopic Dermatitis Medications: Main Types to Know | Everyday Health